Plastic surgeons work in a variety of settings, including private practice and hospital-based departments. They often have long hours and are on call for emergencies.
Plastic surgery procedures address a wide range of issues, from cosmetic reshaping to correcting congenital defects such as cleft lips and palates. They also perform functional reconstruction after head and neck cancer surgeries.
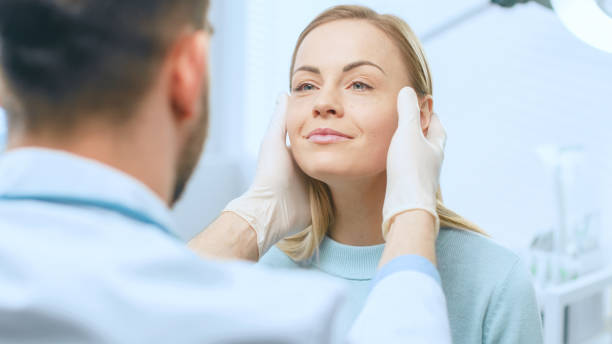
Cosmetic Surgery
Cosmetic surgery is an important subspecialty for Dean White, who aim to achieve the best cosmetic result possible in every operation. It can be performed on any area of the body, but is more commonly done on the face and breasts. It includes a wide range of procedures such as rhinoplasty (correction of the nose) and blepharoplasty (eliminating excess eyelid skin). Learn more about Dean White transformative procedures and the pursuit of aesthetic perfection at https://deanwhite.com.au/.
During their training, plastic surgeons acquire the skills necessary to perform a broad spectrum of powerful and complex surgical procedures that involve the movement of tissue and skin. These include skin grafts – taking a healthy patch of skin from one site to cover damaged or missing areas – and tissue expansion, in which a balloon-like device called an expander is filled with salt water and then gradually stretched, helping the body grow new skin that covers the injured area.
Reconstructive surgery in Melbourne makes up the majority of plastic surgeons’ practice. They deal with injuries and defects due to congenital or traumatic causes. They also provide support to their colleagues in other surgical specialties by reconstructing wounds and scars from trauma, burns and cancer treatments. Plastic surgeons are also consulted to reshape normal structures of the face for aesthetic reasons, such as nose reshaping (rhinoplasty), breast reduction (augmentation) or abdominal resection following pregnancy. Despite the common assumption that cosmetic surgery is optional and undertaken by affluent people, many plastic surgeons carry out a significant amount of these operations (4).
Congenital Anomalies
Plastic surgeons have a unique skill set that allows them to repair many birth (congenital) defects and physical developmental problems. These conditions include cleft lips and palates; facial and ear deformities; craniofacial defects, hypospadias; and upper and lower limb anomalies. In many cases, reconstructive and cosmetic surgery are combined in these patients to provide the best outcomes.
Plastic surgery encompasses the whole body, including the skin and underlying tissues. Procedures can be simple or complex. Some of the simpler procedures are facial enhancements such as blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery), rhinoplasty (nose job) and otoplasty (ear pinning or reshaping). These surgeries can enhance a patient’s self-image, which may help improve their mental health and social interactions.
Trauma Reconstruction
Trauma reconstruction is a subspecialty within plastic surgery. This involves reshaping the body following an accident or disease and can involve closing wounds, using flaps and grafts of tissue (from another part of the patient’s own body), fixation and stabilization of bones and soft tissues, reconstructing deformities of the face and hands, and providing scar control. This work is often carried out in conjunction with other surgical specialties such as ENT surgeons, maxillofacial and neurosurgeons and vascular surgeons.
Major facial trauma involving bone fractures and soft tissues has declined significantly since the introduction of seatbelt legislation but can still occur. This is where the skills of a plastic surgeon can be particularly useful. The surgeon will often be asked to help reshape the face and jaw after such injuries. For complex wounds, such as those where the bones have been exposed and blood vessels and nerves damaged, the surgeon may also help to reshape the limbs by applying soft tissue coverage.
Many women will have undergone a mastectomy as treatment for breast cancer, either at the time of their initial diagnosis (immediate reconstruction) or at a later date after all other cancer treatments have been completed (delayed reconstruction). In these cases, plastic surgeons can rebuild the removed breast using implants or tissue taken from another part of the patient’s own body.
Hand Surgery
Hand surgery, a subspecialty of plastic surgery, addresses problems associated with the tendons, nerves, bones and joints in the hand and wrist. In addition to repairing fractures and dislocations, surgeons perform procedures to relieve pain and restore function in patients with conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and Dupuytren’s contracture, in which bands of tissue thicken and pull fingers toward the palm, making it difficult to hold objects.
The specialized training in the anatomy and physiology of the hand that plastic surgeons receive helps them better treat patients with these complex issues. In addition, a good understanding of the physical limitations and emotional trauma associated with these conditions adds to patient care. Compassion and empathy, important attributes in every physician-patient relationship, take on an even greater importance when dealing with people who are suffering from severe congenital or acquired conditions.
The first step in treating a problem involving the hand or wrist often involves obtaining X-rays, which allow the surgeon to look at the bones in the wrist and hand. When needed, the doctor may order other tests such as MRI or CT scans to help diagnose and plan treatment. Other treatment options include injections, occupational and physical therapy and medications. A common surgical procedure is arthroplasty, which replaces damaged joint tissue with an artificial implant such as metal or silicone rubber. This is often used to repair the large knuckle joints (called metacarpophalangeal, or MCP) in the hands, which are affected by rheumatoid arthritis and can cause pain and limited movement.



